Write component tests for SpringBoot application using OpenTable Embdedded Postgres
I would like to share with you my experience on writing a component test for SpringBoot application using OpenTable embedded Postgres database. I am using Liquibase for database migration. A prior basic understanding of Spring Boot framework is expected from the reader.
For this experiment, I am using:
- Spring-boot 2.3.1 RELEASE
- Liquibase for database migration
- PostgreSQL database for the application code
- OpenTable embedded Postgres for the component test
- Junit 5
The primary focus of this article is to help those poor souls who are in search of a simple and useful article on writing component tests using embedded Postgres database that runs against Liquibase. I have used H2 database previously. I was not very happy with the outcome since I had some unpleasant experiences of the tests passing, but the database migration failing whilst running the migration scripts against a real database. The use of PostgreSQL Test container is another option. Although this is a great approach, sometimes you may be constrained only to use an in-memory option. This happens when your client/employer is using an operating system that is not very Docker friendly. Believe me, this is 2020 and there are companies who are still using Windows 7 operating system!
Architecture diagram
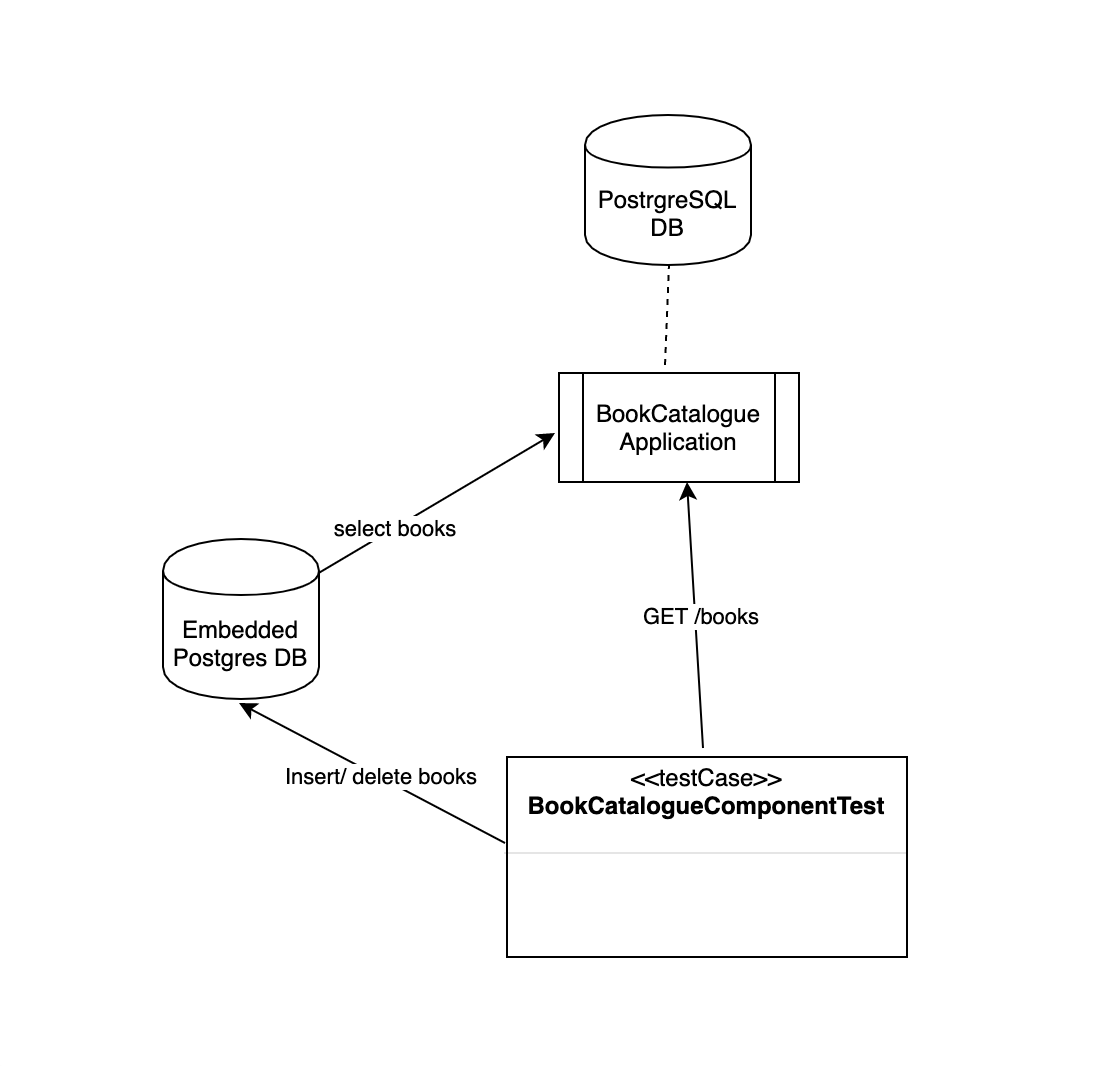
Architecture diagram explained
- BookCatalogueApplication is a SpringBoot application having PostgreSQL as the backend database. The application has a GET /books endpoint that returns a list of books from the catalogue.
- BookCatalogueComponentTest tests the GET /books endpoint and verifies the response body.
- BookCatalogueComponentTest injects the EmbeddedPostgres data-source at runtime. When the component test starts, the first step is to insert the test data in Embedded Postgres database. Because the component test also connects to the same embedded database as that of the application, the GET /books endpoint returns the data that is inserted by the component test.
How to setup the test?
- Firstly, I have created a SpringBoot application called BookCatalogueApplication that uses PostgreSQL database in the backend. I have used Liquibase to do the database migration. The application has a GET /books endpoint, which returns a list of books to the end consumers.
- I have added otj-pg-embedded dependency to pom.xml so that I could use embedded postgres database in my component tests.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.opentable.components</groupId>
<artifactId>otj-pg-embedded</artifactId>
<version>0.13.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- I have also added the following database configuration in the application code.
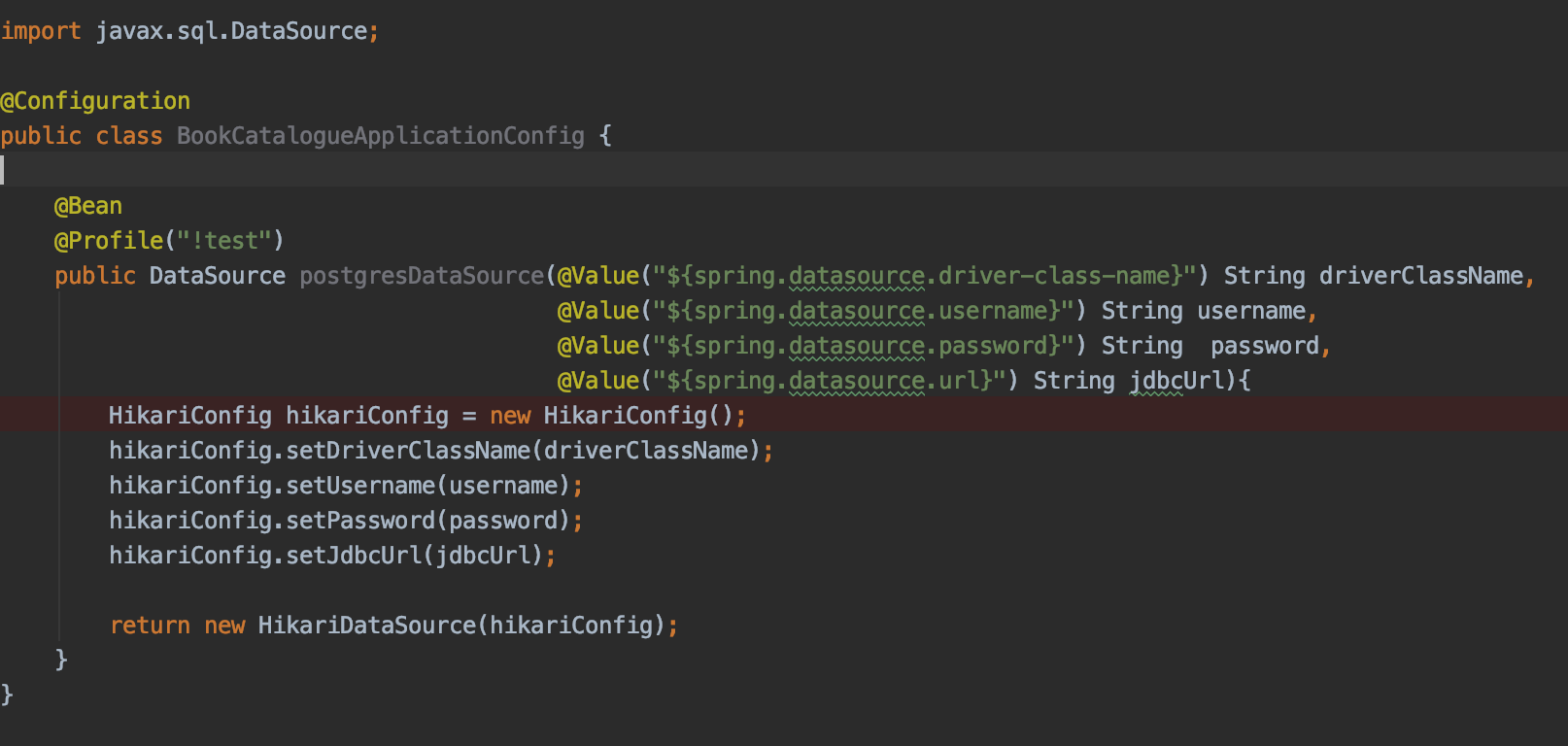
Please note the annotation @Profile(“!test”). The DataSource bean creation will be ignored if the profile is ‘test’. I will take advantage of this by running the component test with ‘test’ profile. This will enable the application code to pick embedded postgres data-source at runtime. - The next step is to add a ComponentTestConfig class. This is the place where we create an Embedded Postgres bean.

The line of code EmbeddedPostgres.builder().start() starts embedded postgres database at a random port.
Unlike H2, OpenTableEmbedded Postgres database can make the component tests slow, especially when there are a large number of tests to run. To speed up the tests, I have added a check to start the database only if the database is not started yet. This will start the database only once for the entire test suite run.
- The next step is to create a component test class called BookCatalogueComponentTest.java.
This is a SpringBootTest with ActiveProfiles set to ‘test’.
@SpringBootTest(classes = BookCatalogueApplication.class, webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) @ActiveProfiles("test") @DirtiesContext public class BookCatalogueComponentTest {...}The application is spun up at a random port. The component test can access the application port by using the following lines of code. This will be useful when we call the GET /books endpoint.
@LocalServerPort
private int applicationPort;
I have injected the data-source in the component test class. This is for loading the test data. This is an optional thing to do and will only be needed if the database pre-population is necessary.
@Autowired
@Qualifier("embeddedPostgresDataSource")
private DataSource dataSource;
In the test, I call the method executeDBQuery(dataSource, INSERT_BOOKS) that loads book data into the embedded database. When the GET /books endpoint is called, those records are returned.
The insert queries are stored in insert_books.sql under the resources/db_queries directory.
The actual test method is very straight-forward.
- It reads the response JSON file as String.
- Then calls GET /books endpoint.
- The response body is then compared against the expected response string and verifies the result.
@Test
public void getBooks_ShouldReturnAListOfBooks() throws JSONException {
//Given
String expectedResponse = readFile(GET_BOOKS_RESPONSE);
//When
ResponseEntity<String> actualResponse = TestApiHelper.getForEntity(applicationPort, GET_BOOKS);
//Then
assertEquals(expectedResponse, actualResponse.getBody(), JSONCompareMode.STRICT);
}
- In the end, the component test calls a tearDown() method, that deletes all the book data that was previously inserted in the embedded postgres database.
This step is especially important if we start the embedded postgres only once. This is to avoid any potential data conflicts if multiple test cases are run one after the other.
@AfterEach public void tearDown(){ executeDBQuery(dataSource, DELETE_BOOKS); }